
Additionally, the PPC can help find the point where a business can optimize its resource use. Importance of the production possibilities curveīusiness leaders and economists use the production possibilities curve to help them make production decisions because when two products share a finite resource. It’s also worth noting that production possibility curves are usually decreasing and concave down to represent the finite outcomes that result from finite resource usage. It consists of several points to indicate the ideal production for a company. Related: Understanding Economics: Indicators, Types and Why Economists Are Important What does a production possibilities curve look like?Ī production possibilities curve is a smooth curve that resides in the positive portion of a graph. Since there is a shared resource between the two items, the graph ends up in the shape of a curve. They continue this exercise until they are down to 0 tomatoes and 50 cucumbers, then draw a line connecting the dots on the graph. After graphing these two points, the farmer calculates how many cucumber plants they could grow if they grew 90 tomatoes instead of 100. For example, a farmer has enough space for either 100 tomato plants or 50 cucumber plants. You calculate other points, based on removing some resources from one product and shifting it to the other. Calculating this amount for both items then gives you the endpoints of your curve. The maximum amount for each item is the amount you can produce if you devote all resources to that one item and zero to the other. You display the potential outputs of each item on the two axes of the graph. Production possibilities curves work by illustrating on a graph the product possibilities frontier. Related: What Is the Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)? How a production possibilities curve works With a production possibilities curve, the government can find the point where it would spend its resources most efficiently. Since devoting resources to one program means there are fewer resources available for the other, the government which program it wants to fund more. It wants to fund two programs with its resources, education and public health. Also known as the production possibilities frontier, the PPC measures the maximum output of two goods based on a fixed amount of input.įor example, the government has a fixed amount of resources in the form of taxes. It helps illustrate the tradeoff between using more resources in one product over another. The production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the different amounts of a product that a business or economy can produce based on a shared resource. What is the production possibilities curve? Any point below point F is considered extreme inefficiency and could be an indicator of a severe recession.At this point, you do not have the needed amounts of resources to produce the number of goods shown.
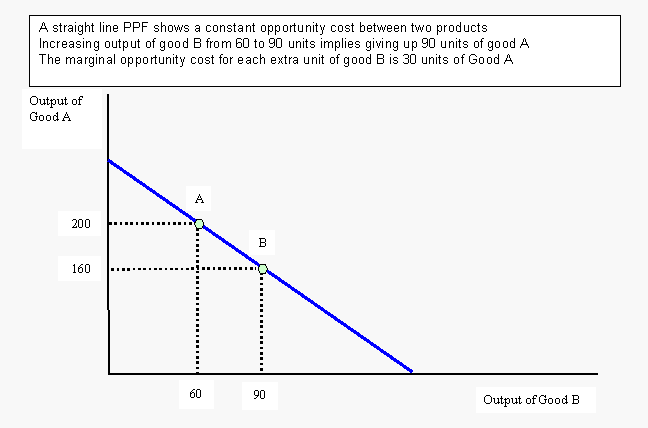
Point G represents a production level that is unattainable.You can produce at this point, but you are not using all your resources as efficiently as possible. Point F in the graph below represents an inefficient use of resources.In the below graph this is represented by points A, B, C, D, and E. This is represented by any point on the production possibilities curve. Productive Efficiency - This efficiency means we are producing at a combination that minimizes costs.If you are given the situation where a particular society needs about an equal amount of sugar and wheat then the allocative efficient point would be C. This is represented by a point on the production possibilities curve that meets the desires and needs of a particular society. Allocative Efficiency - This efficiency means we are producing at the point that society desires.The production possibilities curve can illustrate several economic concepts including: Efficiency For the Production possibilities curve we assume three things when we are working with these graphs:

In eceonomic analysis we have to develop assumptions to be able to draw conclusions. 📈 It shows us all of the possible production combinations of goods, given a fixed amount of resources.

The production possibilities curve is the first graph that we study in microeconomics. Introduction to the Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
